Setup Ripe for Defense Tech Startups to Shine
In an era marked by rising geopolitical tensions and evolving warfare dynamics, the defense tech industry has become a crucial area for investment and innovation. This sector plays a significant role in the US’s efforts to maintain its national security edge against competitors like China and Russia. As a result, venture capitalists (VCs) are increasingly recognizing the immense potential of defense tech startups and are driving their growth with substantial investments.
Over the past three years, VCs have poured nearly $20 billion into aerospace and defense tech startups, according to Pitchbook. This figure is almost four times the amount invested between 2010 and 2019, reflecting the growing interest in this vibrant sector. For example, in May 2023, Andreessen Horowitz announced a $500 million fund to support early-stage companies that “advance the national interest.” Additionally, Pitchbook data highlights that acquisitions made up 71% of defense tech VC exits from 2016 to 2021, emphasizing the strategic value of these startups to larger industry players.
The expansion of these startups can be attributed to their ability to create technologies with dual-use applications, benefiting both military and commercial sectors. By extending their market reach beyond the defense industry, these companies have unlocked new opportunities for venture-worthy growth and innovation. This approach has enabled them to achieve significant growth beyond what could be accomplished solely through government contracts. For instance, Shift5, which recently secured $83 million in a Series B funding round, serves both military units and critical infrastructure operators. The company provides solutions that enhance the monitoring of infrastructure systems, including aircraft, trains, and military weapons systems.
As warfare evolves with advancements such as artificial intelligence, autonomous weapons, and cyber warfare, agility, innovation, and technological expertise are crucial for maintaining a competitive advantage. In response, the Department of Defense is dedicating a significant portion of its $300 billion budget for research, development, testing, evaluation, and procurement to these emerging areas. The government’s focus on national security and the creation of innovation hubs like the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, Defense Innovation Unit, National Security Innovation Capital, In-Q-Tel, and AFWERX have fostered a thriving environment for developing critical technologies, attracting funding, and promoting sector growth. Moreover, capital providers such as the Office of Strategic Capital are bridging the gap between the military, entrepreneurs, and investors.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has also underscored the importance of adopting new technologies in warfare. For US defense tech firms, Ukraine has become a testing ground for their latest innovations. Companies like Maxar Technologies have used AI-enhanced systems to turn satellite imagery into valuable intelligence for Ukraine. Anduril, a leader in the VC-backed defense tech surge, has supported Ukraine with hardware, software, and personnel. Valued at $8.5 billion, Anduril has developed technology that enables a single operator to manage ‘hundreds’ of autonomous systems, potentially revolutionizing Pentagon operations by overcoming budgetary and operational constraints.
AI is also making significant inroads into the defense sector, becoming a vital tool for battlefield decision-makers. California-based Shield AI is developing AI-powered fighter pilots, drones, and defense technologies, serving clients such as the US Air Force, US Army, and Brazil Armed Forces. Washington, DC-based Rebellion Defense leverages AI and machine learning to address defense challenges for the government.
As the Pentagon reformulates its traditionally slow-moving procurement processes and embraces startups, the defense industry is undergoing a remarkable transformation. Pitchbook projects the defense tech market will grow to $184.7 billion by 2027 from $76 billion in 2022, with a 15.9% CAGR, driven by increasing government demand for innovative dual-use technologies. Escalating geopolitical tensions are spurring higher military expenditures, which rose by 3.7% to $2.24 trillion in 2022. This increased demand benefits traditional defense contractors and opens numerous opportunities for technology companies and startups to innovate and compete in the rapidly expanding defense tech market.

Generative AI Regulation – A Delicate Balancing Act
The emergence of new technologies often generates a blend of excitement and apprehension, and the advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are no exception. The rapid development of AI has sparked significant regulatory attention and a thorough assessment of its potential implications.
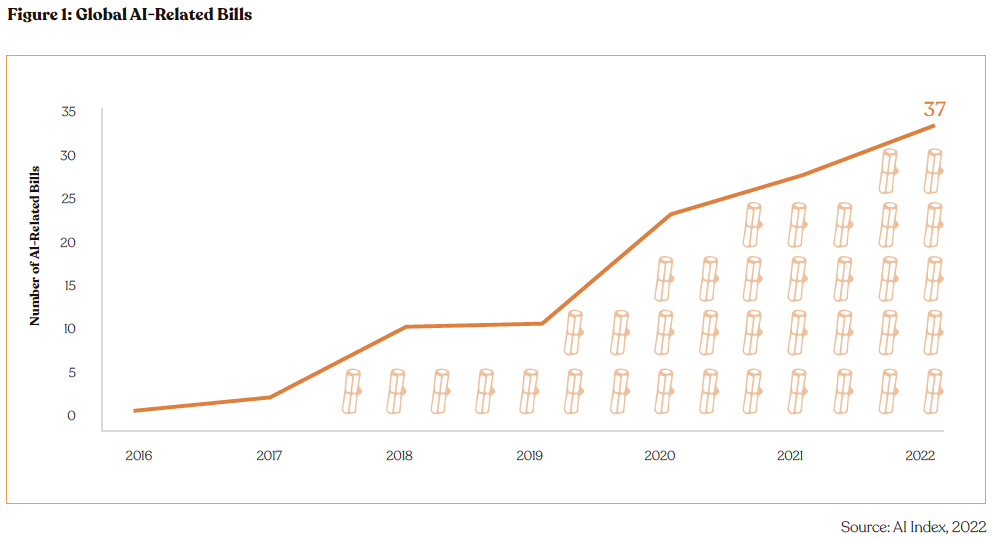
Globally, regulators are making strides toward establishing frameworks for generative AI. Recently, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has been actively advocating for AI regulations, engaging with US congressional leaders from both parties to stress the importance of such measures. In a notable move, the European Parliament’s committee of lawmakers approved the EU’s AI Act in May, bringing it closer to becoming law. This regulation adopts a risk-based approach and includes specific requirements for developers of “foundation models” like ChatGPT, ensuring compliance with copyright laws in their training data. China is also preparing to present a draft of its AI law to its lawmakers for review later this year. Additionally, the Canadian parliament is considering its own contentious Artificial Intelligence and Data Act.
The rapidly changing landscape of generative AI presents challenges for crafting specific and comprehensive regulations that can keep up with technological advancements. Instead of imposing rigid rules, a more effective approach might be to establish guidelines that encourage the responsible development and deployment of generative AI.
While some advocate for a separate regulatory body to oversee generative AI, it’s important to recognize that existing legal frameworks can address AI-related issues without hindering its progress. Laws such as intellectual property rights, privacy regulations, and anti-discrimination statutes are already in place and can be applied to manage potential concerns related to generative AI. US Senator Ron Wyden of Oregon is currently working on the Algorithmic Accountability Act, which would mandate testing of high-risk AI systems before they are deployed.
AI is already subject to considerable regulation, including data protection laws such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation and the US’s Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. These regulations are crucial for protecting personal information and ensuring accountability.
Generative AI is also being applied in highly regulated sectors like healthcare and finance, demonstrating the effectiveness of existing regulatory frameworks in these critical areas. Moving forward, it is essential to have regulations tailored to specific sectors within the AI landscape. As AI technology continues to evolve and integrate into various industries, sector-specific regulations will be crucial for ensuring ethical and responsible deployment. Such regulations should address issues related to privacy, security, transparency, bias, and accountability, among other key concerns.
However, lawmakers need to be cautious of the lobbying efforts from major tech companies like Alphabet, Microsoft, and OpenAI. These companies wield significant resources and political influence, which can impact policy and regulatory decisions. While their contributions to technological innovation are substantial, it is important for legislators to maintain an impartial and objective stance. By critically assessing the lobbying activities of these influential companies, lawmakers can ensure that regulations are designed with the public’s best interests in mind, rather than being swayed by private interests.
The core challenge in the debate over AI regulation is finding the right balance between mitigating risks and promoting growth. This complex task requires a thorough and collaborative approach, involving diverse stakeholders, rather than relying solely on technologists to guide regulatory decisions. Moreno Capital is actively engaged in this discussion, keeping an eye on regulatory developments and working to navigate and adapt to the evolving landscape of AI.

